Need Help NOW? Get a Local Heating Pro Fast!
An electric furnace is an environmentally friendly option, if you can afford the energy costs. Here is how an electric furnace works.
In some regions or circumstances, electricity is the preferred energy source for a forced-air heating system—though electric furnaces are quite uncommon because of the high cost of electricity as a furnace fuel in most regions.
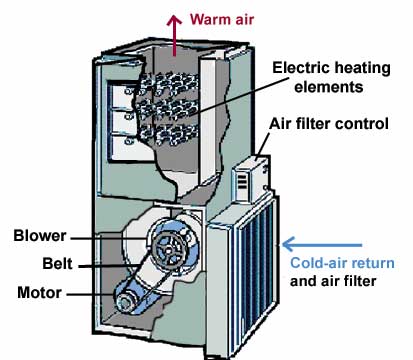
An electric furnace is similar to a conventional gas forced-air furnace except that it produces heat with electric heating elements instead of gas burners. Circuit breakers that control the heating elements may be either inside or outside the cabinet.
An electric-resistance furnace works like a big hair dryer. As with a gas forced-air furnace, it has a blower that draws air into the cabinet through a cold-air return and then pushes the air through the heat exchanger. There, electric heating elements heat the air, and the blower pushes the warmed air back into rooms through a system of duct work.
One advantage of electric heating over gas and other combustion fuels is that electric heating doesn’t give off carbon monoxide. This is good for the environment and makes the unit easier to install because it doesn’t require a flue to carry combustion gases outside. But again, the big downside is the high cost of electricity in most regions. For this reason, heat pumps make more sense if you want to use electricity as a fuel. (For more, see the Heat Pumps Buying Guide.)
Monthly maintenance involves replacing (or cleaning) the air filter, and, if the unit includes a humidifier, cleaning that component.
Most problems are caused by an interruption in the delivery of power, faulty heating elements, or blower breakdowns. Because electric furnaces have a high-voltage hazard inside the cabinet, leave repairs to a qualified HVAC service technician.







 Don Vandervort writes or edits every article at HomeTips. Don has:
Don Vandervort writes or edits every article at HomeTips. Don has: