A heat pump cools and heats a home very efficiently, thanks to the magic of refrigeration technology! Before buying a conventional furnace or AC system, be sure to check out heat pumps.
For homes in climates where cooling and heating requirements are moderate, heat pumps can be a strong energy-saving alternative to conventional forced-air furnaces and air conditioners.
Using refrigeration technology instead of fuel combustion to provide warmth and cooling, conventional heat pumps move heat from cold to warm spaces—and vice versa—to cool a warm house in the summer and heat a cool house in the winter. By transferring heat instead of producing it, they can do their cooling or heating far more efficiently than conventional furnaces and air conditioners.
How to Buy a Heat Pump
Before investing in a new heat pump, it’s important to make sure that it will be right for your home. This will depend upon your climate, energy sources prevalent in your area, and the energy efficiency of your home.
In moderate climates where electricity is used for heating, energy bills can be trimmed by as much as 30 percent to 40 percent. This efficiency drops off significantly at low temperatures because not enough heat can be extracted from the ambient air to provide significant warmth.
In this situation, auxiliary heat from non-efficient heating elements in the system is usually necessary. For more information on buying a heat pump, see the Heat Pumps Buying Guide.
How a Heat Pump Works
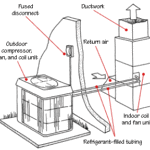
An air-source heat pump, the most common type, works by transferring heat between a house and the outdoors.
Refrigerant travels in tubing that runs between an outdoor compressor-condenser unit and indoor coils mounted on an air handler (like a furnace). Air-source systems require ductwork like that used in a typical forced-air system. If your home lacks this type of ductwork, it can still be heated and cooled by mini-split heat pumps.
An entirely different type of heat pump is the geothermal (ground-source or water-source) heat pump. This type transfers heat between the ground or a nearby water source to your house. Though it can be costly to install, it operates efficiently even in areas with climate extremes.
For more information, see How a Heat Pump Works.
Heat Pump Troubleshooting & Repairs
Heat pumps are sophisticated appliances that can run smoothly for a long time. But every once in a while, like any other appliance, they can break down. They can freeze up, fail to produce heat or cold, trip circuit breakers, and more. For complete techniques on how to fix various types of heat pump problems, see Heat Pump Troubleshooting & Repairs.
Heat Pump Maintenance & Filter Replacement
Though a heat pump operates with very little maintenance, there are a few steps you should take periodically to ensure its best efficiency. Among these are making sure the filters are not blocking air flow and keeping the various components clean. For a look at important heat pump maintenance requirements, see Replacing a Heat Pump Filter.









 Don Vandervort writes or edits every article at HomeTips. Don has:
Don Vandervort writes or edits every article at HomeTips. Don has: