This article introduces the benefits of pellet stoves and wood stoves and guides you to more information about pellet stove buying and installation.
As the price of natural gas and other heating fuels continues to rise, heating our homes is becoming a major budget expense and a significant obstacle to comfort and safety. What can a homeowner do? In the quest for efficient heating, homeowners are turning to combustion stoves that burn wood or wood-like byproducts. These types of stoves are used to provide supplemental (or, in some cases, primary) heat—generally in open-plan homes or in large living spaces.
Combustion wood- and pellet-burning stoves are available in two main types: circulating and radiant. Both are made of an outer cast-iron or steel shell, but circulating stoves have an inner pocket where air is heated and then moves out into the room, and a radiant stove simply absorbs the heat from the fire and radiates it out to the room. Both types are less efficient at delivering heat than furnaces and boilers.
[
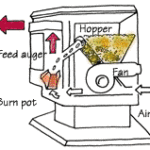
Pellet stoves are similar to wood stoves, but most are far more efficient and burn much more cleanly. They create heat by burning pellets made of recycled sawdust, wood shavings, or other bio-mass waste materials. In comparison to other popular heating fuels such as oil, electricity, and even natural gas, bio-mass pellets are a much more affordable option.
Pellet stoves look similar to wood stoves, but the similarities end there. Inside, they are very sophisticated combustion appliances with blowers and moving parts. To learn more about pellet stoves and their advantages and drawbacks, select the tabs above.
NEXT SEE:









 Don Vandervort writes or edits every article at HomeTips. Don has:
Don Vandervort writes or edits every article at HomeTips. Don has: