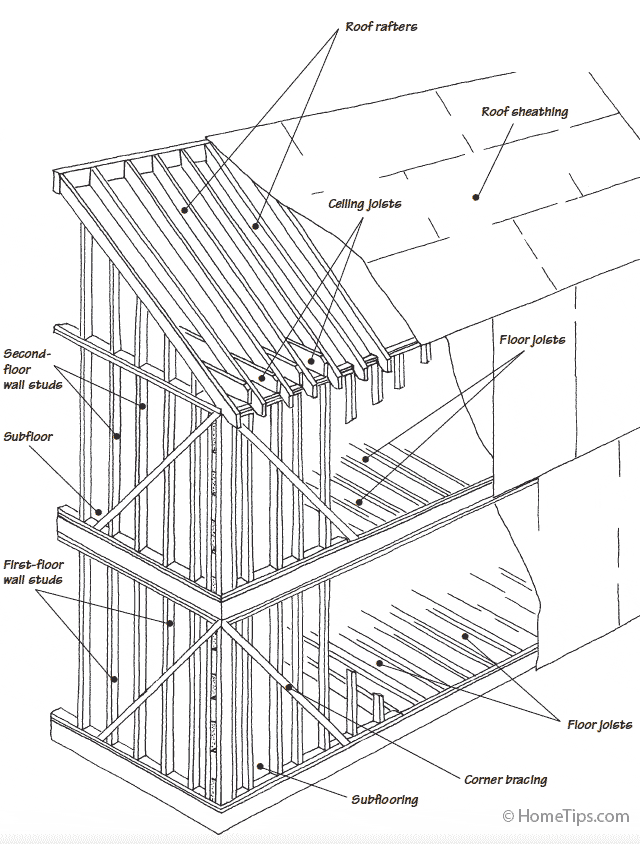
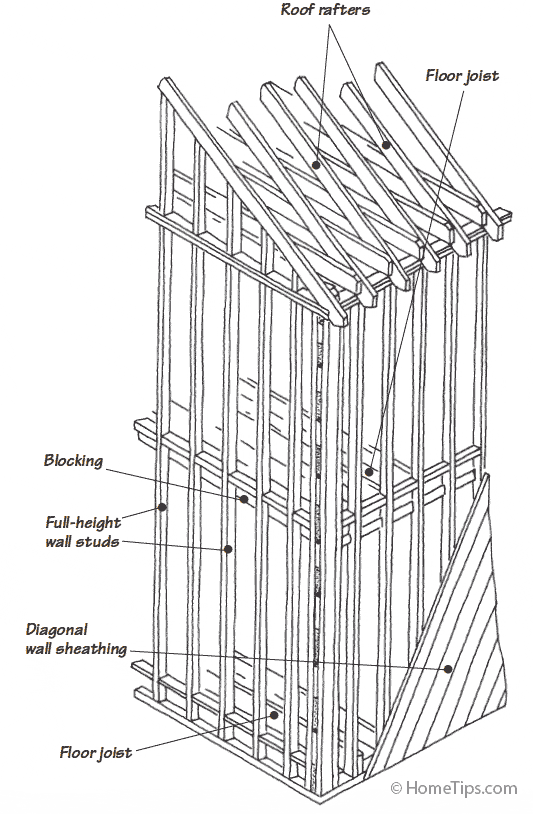
Expert diagrams of the two major types of wood-frame construction for house walls and roofs
Platform Construction
Balloon Framing
Wall-stud Layouts
Wall Sheathing
Roof Sheathing
Overview
| Topic | Description |
| Platform Construction | Walls sit on top of subflooring. Multistory houses are built one level at a time. |
| Balloon Framing | Studs run full height from mud sill to top plate, used for uniform settling in masonry-walled houses. |
| Wall-Stud Layouts | Studs and joists spaced 16 or 24 inches apart, resulting in minimal cutting and waste of materials. |
| Wall Sheathing | Adds rigidity and provides a base for exterior finishes, with newer homes using plywood or composite panels. |
| Roof Sheathing | Provides a base for roofing materials, commonly using plywood or OSB panels for contemporary roofs. |
Two basic methods are used for framing a house: platform and balloon-frame construction. Platform construction is much more common than balloon framing, though balloon framing was employed in many two-story houses before 1930.
Platform Construction
With platform-frame construction, shown below, walls sit on top of subflooring. Multistory houses are built one level at a time with each floor providing a platform for building the next series of walls.
Balloon Framing
With balloon-frame construction, shown below, studs run full height from mud sill to the top plate, to a maximum of 20 feet. This method was popular before the 1930s and is still used on occasion for stucco and other masonry-walled, two-story houses because such structures shrink and settle more uniformly than do platform structures.
But balloon framing is more dangerous to erect because of its weight and height, and the long, straight wall studs required have grown increasingly expensive and difficult to find.
Wall-Stud Layouts
With both platform and balloon framing, wall studs and ceiling and floor joists occur every 16 or 24 inches, measured from center to center. These standardized layouts result in the least cutting and waste of floor, ceiling, and wall materials.
Most older houses have 2-by-4 wall studs spaced 16 inches on center; many newer houses have 2-by-6 wall studs either 16 or 24 inches on center to make exterior walls stronger and create a larger cavity for wall insulation. For more about wall framing, see How to Build an Interior Wall.
Wall Sheathing
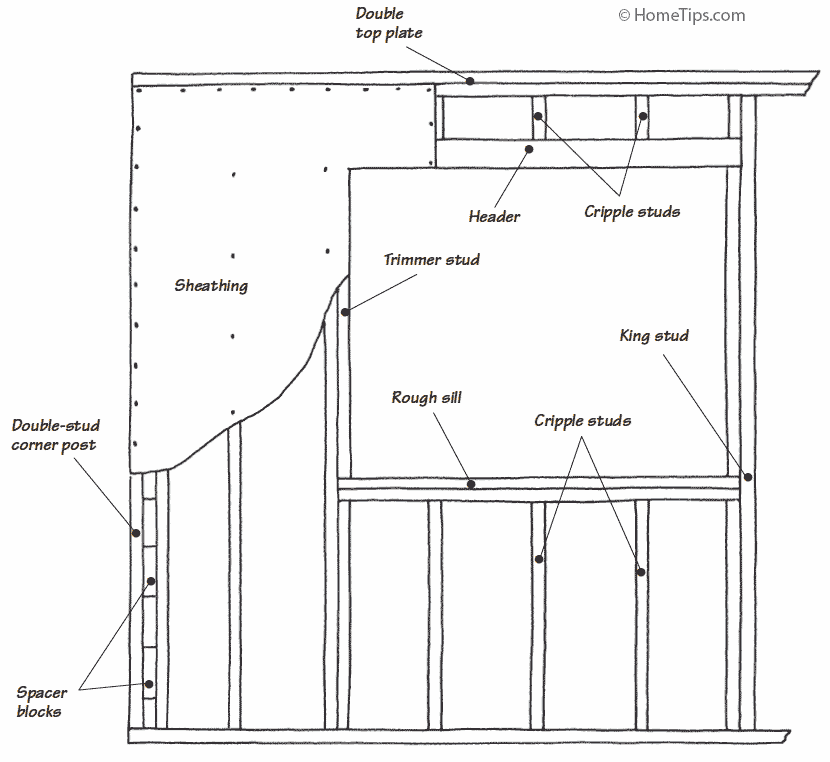
Exterior wall sheathing adds rigidity to the structure and provides a flat base for siding, stucco, brick, stone, and other exterior wall finishes. Older homes have diagonal board sheathing—1/2-inch-thick boards nailed on the diagonal. Most newer homes have plywood or similar composite panel sheathing. For more about this, see Sheathing Exterior Walls.
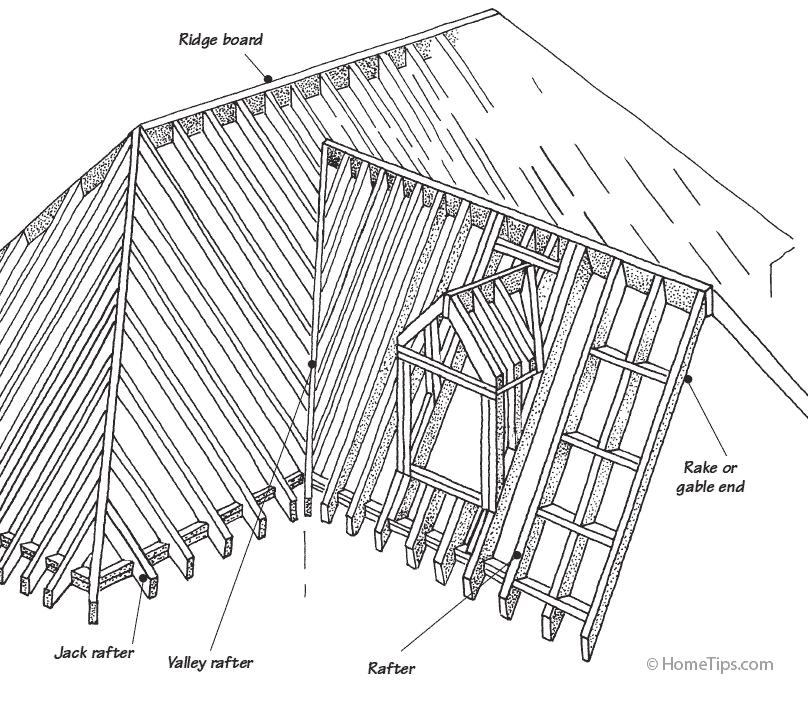
Roof Framing and Sheathing
Roof framing can be quite complex, depending upon the complexity of the roof’s design. Below is the framing for a gabled roof.
Exterior roof sheathing serves the same purposes for roofing materials as wall sheathing does for walls. Most contemporary roof sheathing is either plywood or oriented-strand-board (OSB) panels; spaced wood sheathing is common for wood shingle roofs. For more about this, see Roof Construction Basics.
House Framing Diagrams FAQs
- What is platform construction in wood-frame houses?
Platform construction involves building walls on top of subflooring. Multistory houses are constructed one level at a time, with each floor serving as a platform for the next set of walls.
- How does balloon framing differ from platform construction?
Balloon framing uses wall studs that extend from the mud sill to the top plate, covering the full height of the building, up to 20 feet. This method was popular before the 1930s and is sometimes used in masonry-walled houses because it allows for uniform settling.
- What are the standard wall-stud layouts for wood-frame construction?
In both platform and balloon framing, wall studs and joists are spaced every 16 or 24 inches from center to center. This layout reduces the amount of cutting and waste of construction materials.
- What materials are commonly used for wall and roof sheathing in modern houses?
Modern homes typically use plywood or similar composite panels for wall sheathing to add rigidity and provide a base for exterior finishes. For roof sheathing, materials like plywood or oriented-strand-board (OSB) panels are commonly used, especially in contemporary roofing.






 Don Vandervort writes or edits every article at HomeTips. Don has:
Don Vandervort writes or edits every article at HomeTips. Don has: