Expert advice on how to troubleshoot a furnace that is blowing cold air through air vents. Includes both gas and electric furnaces.
1. Check the thermostat
2. Check pilot light and ignition system
3. Inspect the flame sensor
4. Inspect air filters
5. Verify air vents (registers)
6. Check the ductwork
Have you ever turned up the thermostat on a cold day only to get an icy blast of cold air? Why is there no heat? In this step-by-step guide, we’ll give you basic furnace repair advice for troubleshooting this frosty problem.
What Causes A Furnace to Blow Cold Air?
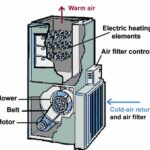
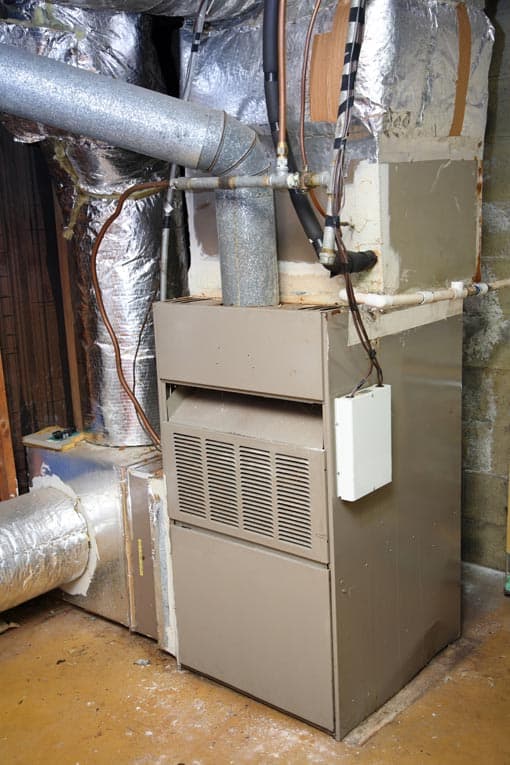
A blower pulls air from rooms, sends it through ductwork to the furnace, and then cycles it back to rooms. As the air goes through the furnace, it’s heated by a gas burner in a gas furnace or electric elements in an electric furnace. If the burner or elements don’t work, the air doesn’t get heated—so it returns to the rooms as a cold breeze instead of warm air.
In gas furnaces, the gas-fed flame must be ignited by a spark or pilot light. If this ignition doesn’t take place, the flame will not ignite and the air won’t get warm.
An electric furnace creates heat more like a toaster—as electricity flows through heating elements, they get red hot. It’s these elements that heat the air as it passes through. If these elements are damaged, are worn out, or have electrical problems, they won’t heat the air passing through the system. The result? Cold or room-temperature air being blown through air ducts and into your rooms.
In both cases, the failure of the heat source is what prevents the air from being properly heated—and in both cases, the furnace blows cold air.If you have a furnace blowing cold air and you want to try to solve the problem yourself, follow these steps.
Note: If you’re unsure about troubleshooting or doing DIY furnace repairs, call a professional HVAC technician.
1. Check the thermostat
First, look at your thermostat settings. Make sure it is set to “HEAT” mode and that the desired temperature (“set temperature”) is higher than the current room temperature. Quite often, a simple thermostat adjustment is all it takes to restore warm air circulation. If the thermostat is set to “COOL” or to “FAN ONLY,” the system will not heat.
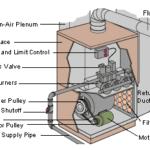
2. Check pilot light and ignition system
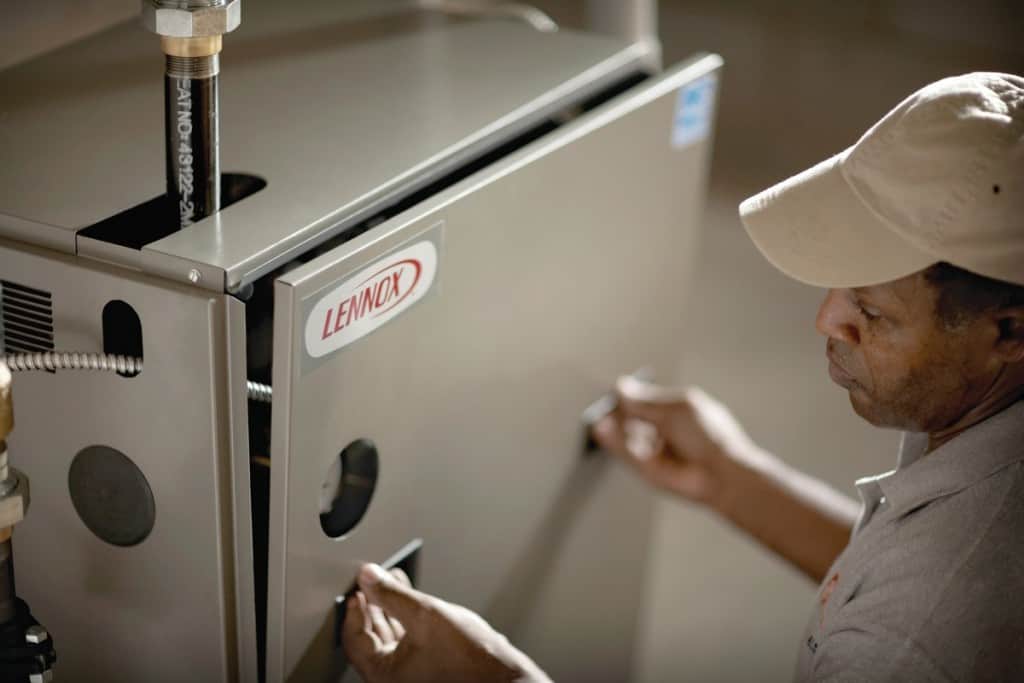
For gas furnaces, a malfunctioning pilot light or ignition system could be the culprit. Look for the pilot light through the little window beneath the heat exchanger and make sure it’s lit. If it’s out, follow the manufacturer’s instructions to relight it safely. If you haven’t done this before, don’t let it intimidate you. It’s a simple task on all modern heaters. For more about relighting the pilot and checking the pilot light assembly, ignition system, or an issue with the gas supply, See Furnace Not Working—No Gas Flame.
3. Inspect the flame sensor
A gas furnace has a flame sensor that shuts off the gas if the flame goes out. This is a safety feature that keeps gas from leaking into the space around the furnace. Sometimes a dirty or faulty flame sensor can shut down the flame. Locate the flame sensor (usually near the burner assembly) and gently clean it using a soft cloth or fine-grit sandpaper. For more detail, see Furnace Heating and Recycling Problems. Note: This step requires fairly advanced DIY skills—if it’s over your head, call a pro.
4. Inspect air filters
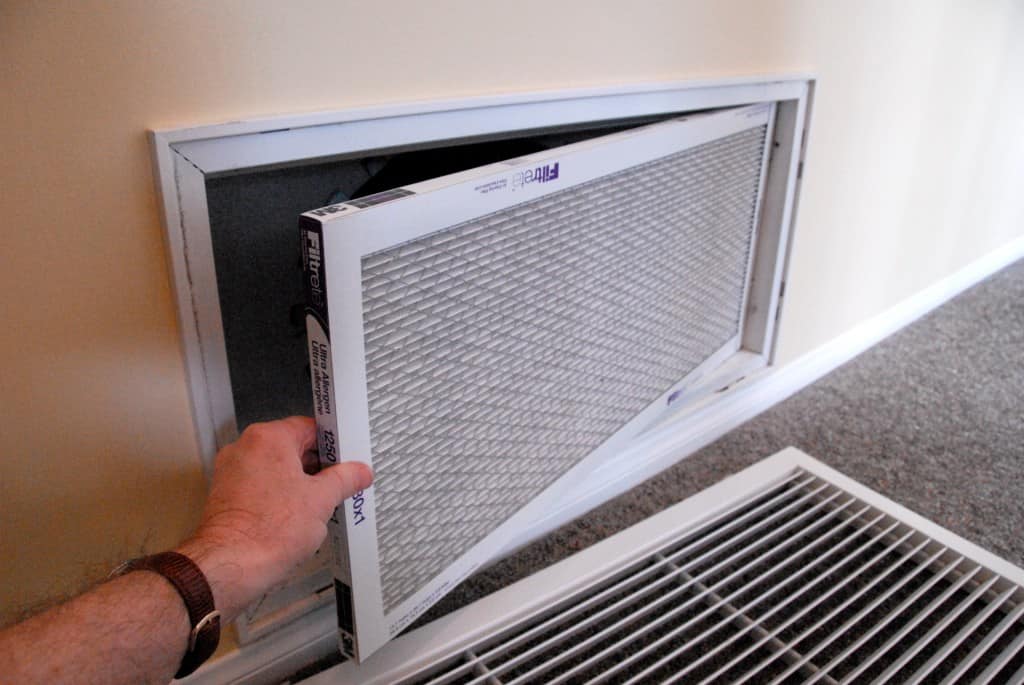
Though it shouldn’t eliminate the heat entirely, a clogged air filter can significantly impact your furnace’s performance when heating your home. Inspect your furnace’s air filter for accumulated dust, debris, or blockages. If it’s visibly clogged with dirt and debris or hasn’t been replaced in 6 months, it’s time for a quick filter change. A clean filter allows for proper airflow, preventing your furnace from working harder than necessary. For more, see How to Replace a Furnace, AC or Heat Pump Filter.
5. Verify air vents (registers)
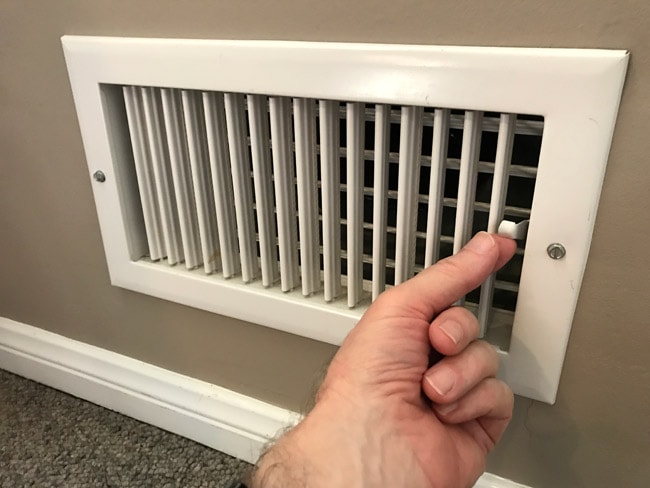
Blocked or closed vents and registers will disrupt the airflow, causing uneven heating or even a complete loss of warm air. Of course, in this case, you won’t feel the system blowing cold air through a particular register—it won’t be blowing any air at all. Make sure all vents and registers are open and not blocked by furniture or rugs.
6. Check the ductwork
Leaky or damaged ductwork can cause warm air to escape, leading to inadequate heating and cold air blowing through your vents. Inspect your ductwork for any visible signs of damage, such as loose joints or gaps. Use duct tape or mastic sealant to seal any leaks or call a professional duct repair service or HVAC technician.
Schedule Regular Maintenance
Prevention is better than having to find a cure. Regular maintenance plays a vital role in keeping your furnace running smoothly for heating your home. We recommend scheduling professional maintenance at least once a year to ensure optimal performance, identify potential issues early on, and avoid surprises like cold air blowing from your furnace.











 Don Vandervort writes or edits every article at HomeTips. Don has:
Don Vandervort writes or edits every article at HomeTips. Don has: